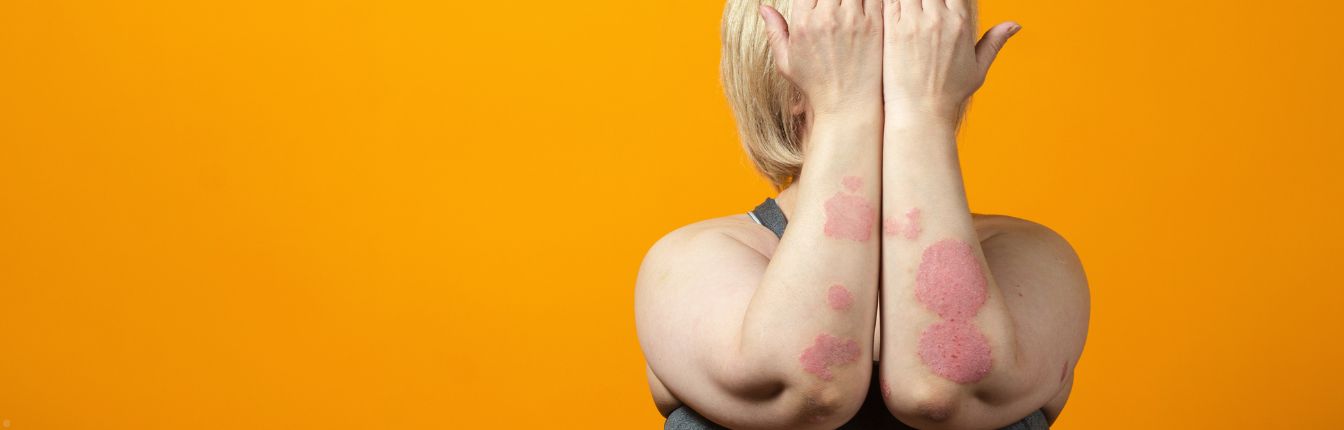
How to Treat an Eczema Rash
Managing eczema requires a combination of medical treatments and lifestyle changes to reduce flare-ups and keep the skin healthy. Below are some of the most effective treatment options available. Keep reading so you know how to treat an eczema rash effectively.
1. Moisturizers and Hydration
One of the most crucial steps in managing eczema is keeping the skin well-moisturized. Thick creams, ointments and lotions can help create a protective barrier that prevents dryness and irritation. Opt for fragrance-free and hypoallergenic products to minimize skin reactions.
2. Topical Corticosteroids
For mild to moderate eczema flare-ups, over-the-counter or prescription-strength topical corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation, redness and itching. These should be used under medical supervision, as prolonged use can thin the skin.
3. Prescription Medications
In cases where eczema is severe or persistent, dermatologists may prescribe medications such as topical calcineurin inhibitors or newer non-steroidal creams like Eucrisa (Crisaborole) to reduce inflammation and itching.
4. Antihistamines
To control itching, especially at night, antihistamines can be used to provide relief. While these medications do not treat eczema directly, they can help prevent excessive scratching that may lead to skin damage.
Related Search Topics (Ads)
5. Lifestyle and Skincare Adjustments
Simple changes in daily habits can significantly impact eczema symptoms. Consider opting some of the following habits into your life:
- Take lukewarm showers instead of hot showers.
- Use gentle, fragrance-free soaps and detergents.
- Wear breathable, cotton clothing and avoid wool or synthetic fabrics that may irritate the skin.
- Maintain a humid environment to prevent skin dryness, especially in winter.
6. Avoiding Triggers
Eczema flare-ups can be triggered by allergens, irritants and environmental factors. Identifying and avoiding these triggers—such as certain foods, pollen, pet dander or stress—can help prevent symptoms from worsening.
7. Phototherapy
For severe eczema that does not respond to topical treatments, phototherapy (light therapy) can be an effective option. This treatment involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision.
8. Biologic Treatments
Newer injectable medications, such as Dupixent (Dupilumab), are now available for people with moderate-to-severe eczema. These biologic drugs work by targeting specific immune system pathways to reduce inflammation.
Signs and Symptoms of Eczema
Recognizing the symptoms of eczema is essential for seeking the right treatment and managing flare-ups effectively. Below are the most common signs of eczema:
1. Itchy Skin
Persistent and intense itching is one of the hallmark symptoms of eczema. Scratching can worsen the condition and lead to skin damage.
2. Red or Inflamed Patches
Eczema often appears as red, swollen or inflamed patches of skin, particularly in areas like the hands, elbows, knees and face.
3. Dry, Cracked or Scaly Skin
People with eczema typically experience extreme dryness, which can cause the skin to become scaly, cracked or even bleed in severe cases.
4. Small, Fluid-Filled Bumps
Some eczema flare-ups result in small, itchy blisters that may ooze or crust over, leading to further irritation and discomfort.
5. Skin Thickening
With repeated scratching and rubbing, the affected skin may become thickened, leathery and darker over time. This condition is known as lichenification.
6. Sensitivity and Irritation
Eczema-prone skin is often highly sensitive and may react strongly to external irritants such as soaps, fragrances, and certain fabrics.
7. Changes in Skin Pigmentation
In some individuals, eczema can lead to patches of skin that appear lighter or darker than the surrounding areas, particularly in those with darker skin tones.
Living With Eczema
Eczema is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management, but with the right treatments and skincare routine, symptoms can be controlled effectively. By recognizing the signs early and taking preventive measures, individuals with eczema can significantly reduce flare-ups and improve their quality of life. If you suspect you have eczema or your symptoms are worsening, consult a dermatologist to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Keep reading to learn about treatment options available for skin cancer patients.
The information on this website is for general educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or qualified healthcare provider before making changes to your health, diet or treatment plan.