Clarity in Comparison
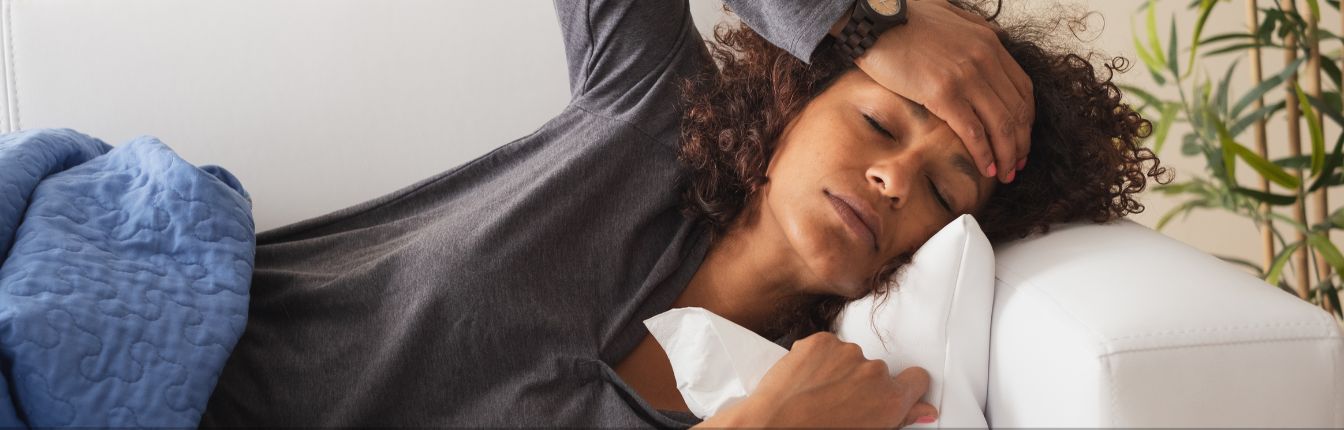
The flu and pneumonia are both respiratory infections ranging from mild to severe. Although they may both cause some similar symptoms, they are two distinct conditions.
It is also helpful to understand the connection between the two respiratory infections. In some cases, the flu can lead to secondary bacterial pneumonia. It is essential to distinguish the flu vs. pneumonia to get proper treatment.
The article below takes a look at what each respiratory infection involves and the difference between them.
What is The Flu?
The flu is a contagious infection caused by a virus. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, there are four types of influenza viruses: A, B, C and D. The flu is a respiratory infection that is easily spread from person to person through respiratory droplets when a person coughs or sneezes.
Symptoms of the flu may come on suddenly and include:
- Fever.
- Body aches.
- Coughing.
- Chills.
- Headache.
Although the flu can become serious, it is usually not the flu infection itself that leads to life-threatening complications. The flu can cause secondary bacterial pneumonia, and it is also possible to become septic from the flu infection.
What is Pneumonia?
Pneumonia involves inflammation of the lungs. The alveoli, which are the air sacs, fill with pus. This can block oxygen flow into the lungs and, subsequently, the bloodstream. In severe cases, pneumonia can cause respiratory failure and death.
Pneumonia may also be caused by a virus. For instance, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is an infection that can lead to viral pneumonia in young children.
However, in addition to viral pneumonia, there are also other causes. Pneumonia can occur as a result of a bacterial or fungal infection. The American Lung Association reported pneumococcal pneumonia is the most common type of bacterial pneumonia.
Pneumonia may also develop if someone accidentally inhales food or drink into their lungs. This is called aspiration pneumonia.
Pneumonia Symptoms
Symptoms of pneumonia may include:
- Coughing that produces yellow or green mucus.
- Fever.
- Chills.
- Shortness of breath.
- Rapid breathing.
- Sharp chest pain.
- Confusion, especially in older adults.
- Low energy.
Several factors affect how serious pneumonia becomes. Factors that influence severity include the germ causing the infection, the person’s age and underlying medical conditions.
The Differences Between Flu and Pneumonia
There are differences between the flu and pneumonia. For example, some of the symptoms may differ. The flu often causes symptoms that affect the entire body. Flu symptoms can include body aches and chills. Pneumonia is a lung infection, so it usually causes more respiratory symptoms.
Additional symptom differences and features that distinguish the flu from pneumonia include the following:
- Fever intensity: The intensity of the fever may differ between both illnesses. Although both can cause a high fever, pneumonia may cause a persistent fever more often than the flu.
- Cough: The characteristics of the cough may also be different. The cough that occurs with pneumonia is often more intense than the cough with the flu. Pneumonia may also cause an increase in mucus. A cough from the flu is often dry.
- Breathing: Breathing issues with pneumonia tend to be worse than with the flu. Shortness of breath and chest pain are usually more pronounced with pneumonia than with the flu.
Diagnosing and Treating the Flu and Pneumonia
The flu is also always called by a virus. Although a virus can also cause pneumonia, it also has other causes, such as bacteria. Pneumonia is also less contagious than the flu.
The onset of the flu and pneumonia also differs. Typically, the flu comes on suddenly, while pneumonia may take a little longer to develop.
Healthcare professionals can perform diagnostic tests to help confirm whether a person has the flu or pneumonia. The tests may include lab tests, such as a nasal and throat swab to check for a viral infection. A chest x-ray also helps identify pneumonia.
Treatment may also differ depending on the cause of pneumonia. For instance, treatment for bacterial pneumonia includes antibiotics. While antibiotics do not treat the flu.
Both conditions may require supportive treatment to ease symptoms, such as breathing treatments and over-the-counter pain medications.
Prevention Methods for the Flu and Pneumonia
Although it may not be possible to prevent all cases of the flu or pneumonia, there are things you can do to reduce the risk.
Vaccines are available each year to reduce the risk of the flu. Decreasing your risk of the flu may also reduce the risk of secondary bacterial pneumonia from developing. A vaccine is also available to help reduce the risk of bacterial pneumonia.
Good handwashing and keeping your immune system strong by getting enough sleep is also helpful. Staying away from people who are sick may also help reduce your risk.
Read on to learn about some of the best foods that help increase blood flow.
The information on this website is for general educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or qualified healthcare provider before making changes to your health, diet or treatment plan.